Graeco-Roman Tombs With Hieroglyphic Texts Found Near Aga Khan
A joint Egyptian-Italian team discovered Graeco-Roman tombs with intact mummies and hieroglyphics near Aswan’s Aga Khan Mausoleum, revealing a hidden layer of Egypt’s ancient funerary landscape.
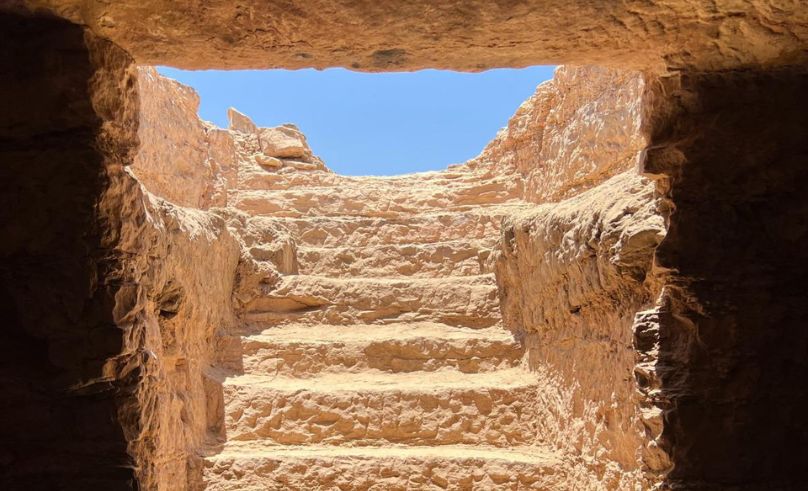

A series of rock-cut tombs dating to the Graeco-Roman period has been discovered near the Aga Khan Mausoleum on Aswan’s western bank. Unearthed by a joint Egyptian-Italian mission, the tombs feature preserved hieroglyphic inscriptions and architectural elements rarely seen in later-period burials.
Among the finds is Tomb No. 38, situated over two metres underground and accessed by a nine-step staircase once used for funeral offerings. Inside, a two-metre-tall limestone sarcophagus rests on a platform carved from bedrock. Decorated with a human-shaped lid, stylised wig, and hieroglyphs, it names the tomb’s owner as Ka-Mesiu, a high-ranking official, and references his family. Several mummies, including those of children, were also found.
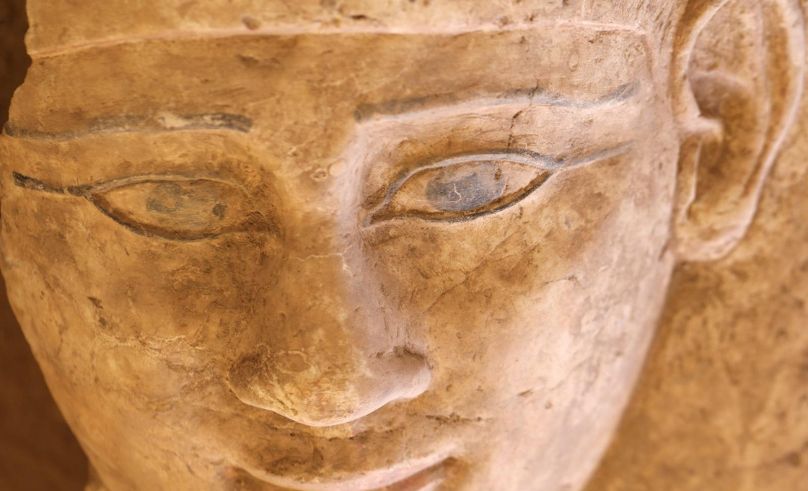

The site continues to offer insight into burial customs of different social classes during a time when Egyptian traditions mingled with Greco-Roman influences. The surrounding necropolis has been under study since 2019, with prior seasons revealing additional tombs and platforms carved into the slopes of nearby Sidi Othman mountain.
The mission, led by Egypt’s Supreme Council of Antiquities and the University of Milan, plans further analysis including CT scans and biological studies this autumn to deepen understanding of the individuals buried there.
- Previous Article Newly Upgraded Dubai Fountain Will Come Back to Life This October
- Next Article Inside Egypt’s Seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites